By wordpress
THE HOTTEST AI POTENTIAL
INTEGRATION WITH DATA PLATFORMS
Data platforms are the foundation upon which artificial intelligence (AI) systems are built. High-quality data and effective data management ensure that virtual assistants operate optimally and deliver accurate, relevant information to users.
With the rise of tools like ChatGPT and large language models, generative artificial intelligence (genAI) has become one of the most influential technology trends of recent years. genAI tools are now part of daily workflows for many employees, and more organizations are exploring how to leverage them to optimize work processes, automate repetitive tasks, and reduce workload.
One of the most common business applications of genAI is intelligent virtual assistants. From a technical standpoint, these are relatively straightforward solutions addressing specific business challenges. They are often used to help employees search internal documentation, support customers with frequently asked questions, or assist with client communications.
However, genAI’s potential goes far beyond chat-based assistants. Its real power emerges when integrated with connected technologies like data platforms and internal systems. To maximize performance, it’s wise to also include other AI approaches, such as traditional machine learning.
Intelligent Virtual Assistants – A Better, Personalized User Experience
Intelligent virtual assistants are available 24/7. They can guide users through the process of retrieving information, resolving issues, and help them find answers or solve problems without human intervention. They are designed to handle routine and repetitive tasks, enabling people to focus on the more complex and value-added aspects of their roles. This includes tasks requiring emotional intelligence, creativity, critical thinking, and complex problem-solving.
These assistants simulate human-like conversations with users via text-based chat interfaces. In the early development stages, virtual assistants were mostly rule-based systems that relied on pattern recognition. These systems responded to user input based on a predefined set of rules, following decision trees or process diagrams. They were programmed to detect specific keywords or patterns in user messages and to generate predefined responses accordingly.
With the integration of machine learning, natural language processing, and deep learning techniques, development has progressed toward the creation of more intelligent and adaptable assistants. The focus has shifted to improving natural language understanding and enabling responses that are more context-aware and capable of inference. Future trends for large language models are headed in the direction of multimodal models—that is, integrating text with other forms of data like images, audio, and video.
One of the most obvious advantages of intelligent virtual assistants is their ability to chat with multiple users simultaneously and deliver responses within seconds. This enables immediate replies and reduces customer support response times. These assistants can access multiple types of data sources—such as CRM systems, website content, internal documentation, or so-called knowledge bases.
This provides users with a more personalized and effective experience. Virtual assistants can be integrated with a wide range of communication channels and platforms, including websites, social media, and messaging apps. This way, users and customers can interact with a company through their preferred communication channels. If the assistants are designed for internal use by employees, they can be seamlessly integrated into conversational interfaces like Microsoft Teams, avoiding an overload of different applications and making new technologies more accessible.
When implementing generative AI into business workflows, data and conversation security is of utmost importance. Virtual assistants developed using Microsoft Azure services ensure that confidential data and conversations are not used to train large language models, and when properly developed, the security of the backend application running the virtual assistant is also guaranteed.
Integration with Data Platforms – Connecting Data Across Sources
Despite the growing popularity of the conversational virtual assistants described above, they represent only a fraction of the potential that (generative) artificial intelligence can achieve.
In a world where data plays a key role in decision-making, the integration of advanced technologies—such as generative AI—with data platforms (e.g., Microsoft Fabric) is becoming increasingly important. Data platforms are the foundation on which AI systems are built, and high-quality data along with effective data management ensures that virtual assistants operate optimally and deliver relevant information to users.
GenAI not only improves interaction between users and data, but also enables the transformation of unstructured data (text, images, etc.) into structured formats that can then be stored on data platforms. This is crucial for optimizing repetitive tasks, saving employees from having to search for and manually enter data. Furthermore, this process can be automated to the extent desired by each individual company. The automation can be fully end-to-end, or adapted to include human oversight and intermediate review stages for the data.
Tools like Microsoft Fabric and Microsoft Azure enable the development of data flows that transfer data between various systems. These include systems required for running genAI-based solutions and systems already familiar to employees (such as SharePoint or Excel).
Modern data platforms offer users extensive functionality to gain deeper insights—without the need for additional tools. Microsoft Fabric, for instance, connects data from different sources and includes capabilities for reporting and advanced analytics. It also supports machine learning projects in a similar way to Azure ML Studio.
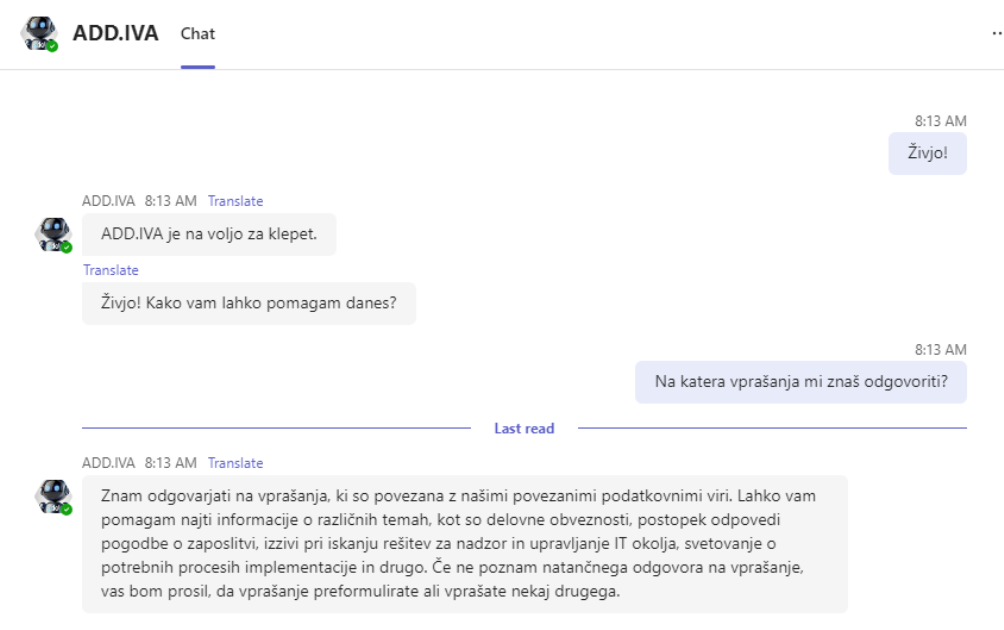
ADD.IVA is a virtual assistant that can be integrated into instant messaging platforms, including Microsoft Teams.
Multi-Agent Systems – Simplicity, Multifunctionality, and Full Customization
Despite the user-friendly nature of such platforms, it is essential to bring data insights closer to users in a fast and simple way. Virtual assistants are ideal in this context, as they enable interaction across various systems through a single interface and can perform background tasks seamlessly.
Virtual assistants designed in this way are also known as multi-agent systems, where all functionalities are triggered based on user input (questions or commands directed to the assistant). Since all communication with the assistant takes place via a conversational interface, users benefit from a smooth experience without the need to switch between systems and technologies. Based on the user’s input, various agents are activated in the background to execute tasks. Status updates and requested data are then returned via the main user interface, powered by large language models.
Examples of technologies compatible with intelligent virtual assistants include:
- Large databases and database operations (e.g., retrieving or entering data):
A practical use case could be registering a new user. The agent checks whether the user already exists in the internal system; if not, it inputs the user’s data (entered through the interface) into the database. - Traditional machine learning models:
A user asks the assistant to classify a specific document, and the agent performs classification using a pre-trained ML model. - Computer vision:
For example, the assistant informs the user about current road conditions, using data obtained from a computer vision model. - Web tasks:
The assistant retrieves information about flight status and prices and, based on the user’s response, can automatically book the selected flight.
These multi-agent systems are capable of performing diverse tasks, such as launching data pipelines, entering data, generating reports, delegating tasks based on previously established criteria, informing, sending notifications … These tasks can also be carried out at a level of automation that is aligned with the business process. The main advantages of a multi-agent system are thus:
simplicity – communication in natural language with a single user interface,
multifunctionality – executing multiple tasks in the background,
complete customization – all multi-agent systems are developed in accordance with the wishes and needs of the clients.
Authors:
Branka Virtič – Head of Data Science
Lučka Guna – Data Scientist at ADD